The highway of the upright is to depart from evil:
he that keepeth his way preserveth his soul.
–Proverbs 16:17
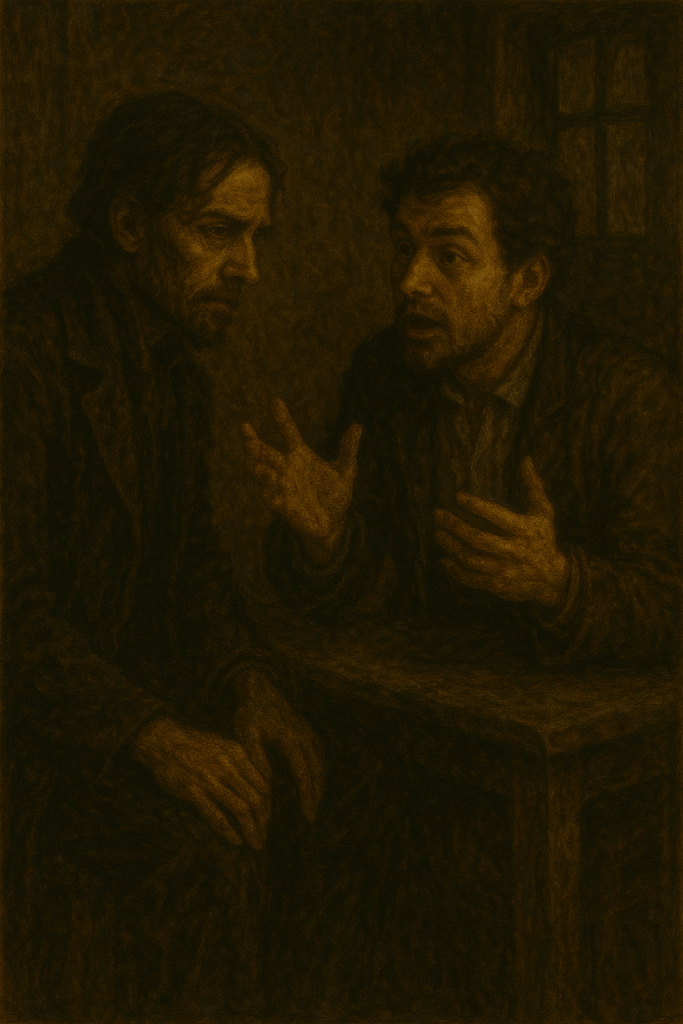
Most novels proceed as a river does—flowing from source to mouth, obedient to the order of time, accumulating its inevitable dams, docks, and diversions along the way. The Idiot, however, is no such river. Dostoevsky drops his protagonist into the current not to drift but to disturb, thus revealing the eddies and whirlpools that form around innocence when it trespasses into the murky waters of high society. That first drop lands Prince Lev Nikolaevich Myshkin—and by extension, the reader—on a train bound for Petersburg. He is fresh from a Swiss sanatorium, where for four years he has been treated for epilepsy. His fellow travelers—Parfyon Semyonovich Rogozhin, newly enriched and drunk on inheritance, and the gossiping Lukyan Timofeevich Lebedev—are the first to be caught in his wake. Rogozhin, with the tactless curiosity of a man ruled by appetite, asks whether the prince is a “fancier of the female sex.” When Myshkin denies it, Rogozhin replies, “[Y]ou come out as a holy fool, Prince, and God loves your kind!” Thus is the first stone cast into the still pond of Myshkin’s effect, its ripples reaching outward in mockery and awe alike.
Soon, the prince finds himself in the home of Ivan Fyodorovich Epanchin, though it is toward Epanchin’s wife, Elizaveta Prokofyevna, that his lineage tenuously connects him. Within moments, he becomes an object of curiosity, as if his very simplicity were some divine riddle. The Epanchins and their daughters draw near him not from affection but fascination; his every word seems to hang in the air long after it has been spoken. So begins the novel’s great fractal of human encounters, each scene branching into another with the stubborn logic of fate.
Translator Richard Pevear observes that, though The Idiot is unanchored to place, it is never abstract. Every room, every parlor and garden, serves as a shell into which the living organism of the narrative crawls. The spaces are cramped, yet within them Dostoevsky builds an architecture of the soul. Each wall is a moral boundary, each window a glimpse into depravity.
The most cavernous of these shells is Lizaveta Prokofyevna herself—“a hotheaded and passionate lady,” who, “without thinking long, would sometimes raise all anchors and set out for the open sea without checking the weather.” In her temperament, we glimpse the embryonic forms of her three daughters: the sensible Alexandra, the artistic Adelaida, and the beautiful, capricious Aglaya. Orbiting them are other satellites of this anxious universe: Rogozhin, the merchant whose newfound wealth becomes license for cruelty; Lebedev, the self-proclaimed “professor of the Antichrist,” who reads the signs of apocalypse in the iron veins of Europe’s railroads; and, most haunting of all, Nastasya Filippovna Barashkov, the fallen specter, whose trauma becomes the crucible of the entire tale. She is distance made flesh: adored by men, despised by women, yet pitied by both.
At the trembling center of this constellation burns Myshkin himself—a sun both fragile and inexhaustible. His presence exposes others as a mirror does, revealing the distortions they cannot bear to face. “I really came only so as to get to know people,” he says to the Epanchins, a confession so plain it becomes profound. In that aim to understand the human heart lies the novel’s central pulse.
From his first conversation, Myshkin unveils the spiritual burden of consciousness. He speaks of men awaiting execution, drawing on Dostoevsky’s own brush with the firing squad: “Take a soldier, put him right in front of a cannon during a battle, and shoot at him, and he’ll still keep hoping; but read that same soldier a sentence for certain, and he’ll lose his mind or start weeping.” The words tremble with prophetic weight, foreshadowing the undoing of characters condemned not by law but by their own desires.
Lizaveta and her daughters listen as if to a visitation. Myshkin, recalling his lonely youth, declares, “Nothing should be concealed from children on the pretext that they’re little and it’s too early for them to know. What a sad and unfortunate idea!” Yet the world he enters treats him precisely as such a child: harmless, ignorant, to be humored and dismissed. “The risen sun,” the narrator tells us, “softened and brightened everything for a moment,” and so it is with Myshkin: his light briefly transforms, though it cannot redeem.
When he first beholds Nastasya’s portrait, he perceives in her a soul both contemptuous and simple-hearted, “filled with suffering.” Her name, from anastasis (resurrection), bespeaks her torment: the lamb whose innocence was traded for the amusement of nonbelievers. Like him, she is called “crazy,” though her madness is but the logical end of a world that mistakes cruelty for sophistication.
Even Myshkin’s name bears contradiction: from mysh, meaning “mouse,” and Lev, or lion. In Dostoevsky’s notebooks, beside sketches of the novel, appear two words umbilically connected: “Prince-Christ.” And yet, Myshkin does not forgive sin; he merely reveals it by existing. To Nastasya, he says, “I am nothing, but you have suffered and have emerged pure from such a hell, and that is a lot.” Thus, he grants her what theology cannot: recognition.
His influence spreads like contagion. “I believe God brought you to Petersburg from Switzerland precisely for me,” exclaims Lizaveta, and though she speaks in self-interest, she unknowingly sheds veracity. Myshkin is brought not for one but for all. When he visits Rogozhin’s home, he beholds a copy of Hans Holbein the Younger’s Christ in the Tomb, that merciless painting of the dead Savior, devoid of light or transcendence. “A man could even lose his faith from that painting!” says the prince. Rogozhin, missing the irony, takes him at his word. Myshkin explains: “[H]owever many books I’ve read on the subject, it has always seemed to me that they were talking or writing books that were not at all about that.” He concludes that “the essence of religious feeling doesn’t fit in with any reasoning… there’s something else here… that atheisms will eternally glance off.” Dostoevsky thus holds up the Russian heart, trembling with contradictions, as both the disease and the cure: a heart that forgets the Father even as it cries out for Him.
If The Idiot has often been called satire, it is only because its realism is too acute to endure. It captures the narcissism of the upper classes with the precision of a surgeon and the patience of a saint. Myshkin’s self-awareness is his shield: “What sort of idiot am I now, when I myself understand that I’m considered an idiot?” he asks, deflating mockery by acknowledging it. Like Eminem’s self-flagellation in 8 Mile—if one may indulge a modern echo—he disarms his accusers through confession, transforming insult into revelation. What they cannot abide is not his foolishness but his love.
This love, however, is tested to absurdity. When an impostor by the name of Antip Burdovsky demands a share of the prince’s inheritance under false pretenses, Myshkin offers it anyway. Though exposed as a fraud, Burdovsky still receives the prince’s charity, for in Myshkin’s eyes, deceit and misfortune are twins. Such naivety is his virtue, his madness, and his crown of thorns.
In a later gathering, one Evgeny Pavlych recounts a murder trial in which the lawyer excuses the killer’s actions as “natural” under poverty. This comment provokes nods and murmurs of agreement among those assembled, to which Lizaveta responds by accusing them of being vainglorious madmen who have turned their back on God and Christ. She lambastes them for harping on the “woman question,” which haunts the novel with its articulation of women’s desires vis-à-vis the men in their lives: “You acknowledge that society is savage and inhuman because it disgraces a seduced girl… But if she’s been hurt, why, then, do you yourselves bring her out in front of that same society and demand that it not hurt her!” It is a sermon worthy of record, and yet it vanishes in the noise of polite indifference.
Among the assembled is Ippolit Terentyev, a dying youth whose intellect burns as his body fails. His “Necessary Explanation,” a swan song in letter form that he insists on reading aloud, is both confession and defiance. “People are created to torment each other,” he proclaims. Confronting the same Holbein painting, he asks, “[H]ow could they believe, looking at such a corpse, that this sufferer would resurrect?” and later, “Can something that has no image come as an image?” For Ippolit, faith is cruelty postponed. “Let consciousness be lit up by the will of a higher power,” he muses, “and let that power suddenly decree its annihilation… let it be so.” His despair is a dark parody of Myshkin’s compassion: both see too clearly to live comfortably among men.
Myshkin, whose “head worked quite distinctly, though his soul was sick,” stands apart. Love is denied him not by fate but by incompatibility with a world that feeds on contradiction. His tenderness for Aglaya withers into disillusion; his pity for Nastasya curdles into dread. Like a puzzle piece that almost fits, he must be left aside until the picture itself changes.
And what of the others? They collapse one by one under the weight of their vanity, leaving the prince almost alone, a gold-foiled icon among ruins.
In one of the novel’s most terrifying moments, Dostoevsky describes Myshkin’s seizure: “A dreadful, unimaginable scream, unlike anything, bursts from the breast… it may even seem as if someone else were screaming from inside the man.” The cry is metaphysical; it is the scream of all creation recognizing itself. To read The Idiot is to experience that seizure, to awaken, trembling, in the aftermath of one’s own delusions. Its absurdity, like its truth, is more real than reality itself. Dostoevsky does not offer resolution; he offers revelation. And when we close the book, the echo of that scream remains: terrible, holy, and alive.